- When Should Children Begin to Practice Handwriting?
- What Are the Most Common Handwriting Problems?
- Finger Exercises to Improve Children’s Handwriting
Are you concerned about your child’s handwriting skills? Handwriting difficulties affect up to 25% of school-aged children. However, early handwriting is more than just putting words on paper. It’s a fundamental skill that impacts future academic success and confidence in your communication.
Handwriting proficiency in children is linked to improved reading comprehension and cognitive development. So when should your child start practicing handwriting? What are the common problems associated with handwriting?
At Ability Rehabilitation, we understand the importance of developing fine motor skills in children for better handwriting. Here, we provide tips to aid your child’s handwriting skills so you can help them improve.
When Should Children Begin to Practice Handwriting?
 Handwriting is a fundamental skill for daily tasks such as writing papers, completing job applications, or making grocery lists. However, it’s also one of the first skills to decline in children with learning disabilities.
Handwriting is a fundamental skill for daily tasks such as writing papers, completing job applications, or making grocery lists. However, it’s also one of the first skills to decline in children with learning disabilities.
The act of handwriting involves a combination of fine motor control and visual-motor integration. Therefore, difficulties with handwriting often indicate challenges in other areas as well.
It’s beneficial for children to begin practicing handwriting when they can hold a pencil and form letters on paper. Starting early increases the likelihood of developing strong writing skills later in life.
While the recommended age for starting handwriting practice is around five, readiness can vary among children. If your child is not displaying signs of readiness, there’s no need to worry. It’s always early enough to begin practicing.
If problems persist with your child’s motor skills and handwriting development, you can always talk to an occupational therapist at Ability Rehabilitation for a customized therapy plan.
What Are the Most Common Handwriting Problems?
The primary issue associated with handwriting often stems from the inability to hold a pencil correctly and form letters accurately. This problem can result from various factors, including an improper pencil grasp, limited control over hand movements, illegible handwriting, and subpar penmanship skills.
Multiple factors contribute to children’s struggles with handwriting, including:
- Poor motor coordination
- Insufficient practice
- Inadequate instruction in handwriting techniques by educators
These challenges can manifest in several ways, such as:
- Messy handwriting
- Substandard penmanship
- Difficulty forming letters accurately
- Inability to write legibly or at all
The encouraging news is that these issues are resolved with targeted intervention and practice.
Finger Exercises to Improve Children’s Handwriting

Let’s explore how finger exercises can aid in enhancing your child’s handwriting:
Finger Pinching
This finger exercise benefits children by pinching a small object by engaging the thumb, index finger, and middle finger. It helps develop fine motor control, which is essential for holding objects between fingers. Incorporate this exercise with a writing activity like drawing a dot or line.
This exercise strengthens finger muscles, promotes a firm pencil grip, and enhances dexterity. It also improves fine motor skills and coordination.
Here’s how to do it:
- Place a small object (like a coin or dried bean) between your thumb, index finger, and middle finger.
- Close your hand around the object.
- Pinch! You can perform this exercise with both hands to enhance each hand’s strength.
To improve their grip, repeat this exercise ten times or as often as possible. It can be done one hand at a time for younger children to simplify it.
Counting with Your Fingers
To aid your child in learning to count, introduce a simple activity using a marble. Place the marble on a flat surface, and encourage your child to pick it up using only their thumb, index finger, and middle finger. Prompt them to count how many fingers they used and repeat the process while visually observing their hands. This activity helps them associate fingers with numbers and reinforces counting skills independently.
During playtime with toys or building blocks, engage your child in identifying numbers by holding up one finger for each item being counted. For instance, they can say, “I see two blocks on the floor!” Then, encourage them to continue counting, saying “three” when there are three blocks, and so on until all items are counted sequentially from 1 to 10 (or any suitable number range for your child).
Strengthening With Clay or Play Dough
Engaging with playdough or clay can be an effective method for children to enhance their finger strength. Younger children should be encouraged to sculpt letters directly into the playdough, and older children can benefit from using a ruler to guide straight lines.
Utilizing playdough offers several benefits for handwriting practice: its pliable texture makes it easy to manipulate, and its array of vibrant colors adds an element of fun to the activity!
This hands-on exercise enables children to refine their fine motor skills while crafting letters. It is a valuable tool for preschoolers and kindergarteners to enhance handwriting in a relaxed home environment.
Write Letters in Sand
Harness your child’s love for sandbox play as a learning opportunity! Lay a sheet of paper in the sandbox and encourage them to draw using their finger or a stick. Ensure they focus on forming letters in the sand rather than random lines. The tactile sensation of the sand can assist them in gaining a better understanding of letter placement on a page as they engage with their writing tools.
While this activity may require more effort from your child, it is an excellent means of refining their motor skills and fostering core strength development.
Finger Writing
This finger exercise is perfect for children as it solely relies on finger movements, excluding using pencils or paper. Your child can independently familiarize themselves with writing letters and numbers while gaining valuable practice for writing tasks.
Here’s how to do it:
Encourage your child to trace each number or letter using only their fingers. If they encounter difficulty with certain characters, utilize a mirror to provide them with a view of the correct orientation of each character. This method enables them to perceive each letter’s appearance from various angles, including above, below, and from the side.
Chores
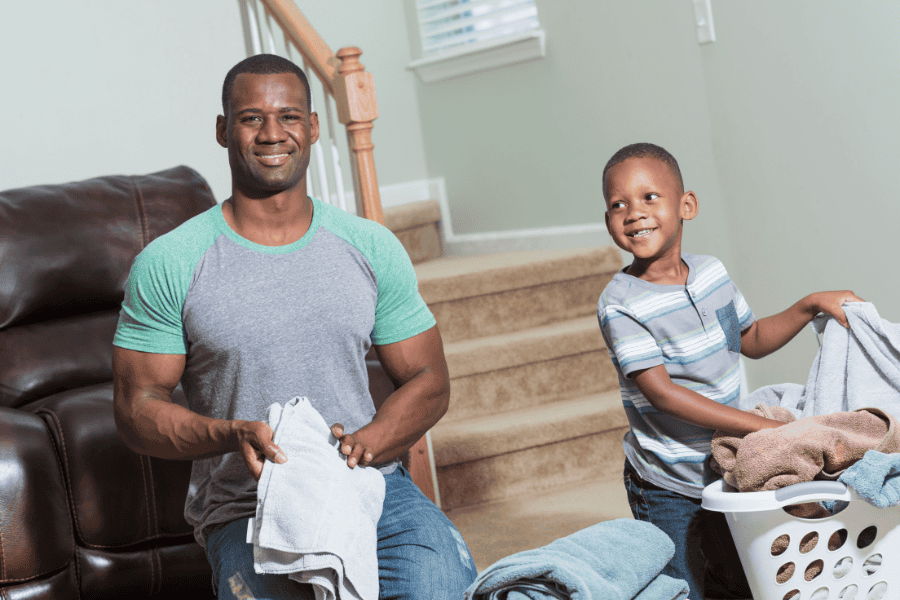 Assigning chores is an effective method to incorporate handwriting practice into your child’s routine. Handwriting proficiency holds significant importance in academic and professional settings, making it advantageous to introduce it early on.
Assigning chores is an effective method to incorporate handwriting practice into your child’s routine. Handwriting proficiency holds significant importance in academic and professional settings, making it advantageous to introduce it early on.
Engaging children in household chores fosters a sense of responsibility, enhances their motor skills, and cultivates a positive attitude toward work and life. Certain chores instill self-care habits and promote tidiness by encouraging children to maintain cleanliness in their surroundings.
Select age-appropriate chores tailored to your child’s capabilities and the household’s needs. Tasks like tidying up after meals or assisting with laundry facilitate skill development while contributing to the household’s upkeep. Chores provide opportunities for children to reflect on their actions, make decisions, and hone essential life skills such as planning, organizing priorities, and problem-solving.
Draw a Straight Line
This straightforward finger exercise is an excellent starting point for your child’s handwriting practice journey, offering ample opportunities for repetition until mastery is achieved.
Drawing a straight line serves as a fundamental skill in developing a steady grip, laying the foundation for creating horizontal and vertical strokes with ease.
Encourage your child to utilize a chalkboard or whiteboard to draw a straight line from top to bottom or side to side. Encourage them to practice these movements repeatedly until they feel confident.
Transition to practicing on paper by providing a ruler or stencil as a guide. This ensures that your child follows the lines accurately as they draw, benefiting both left-handed and right-handed writers in their handwriting endeavors.
Pencil Grasp Exercise
Holding the pencil correctly between the thumb and index finger is essential to develop a tripod grasp.
- Position the pencil in the middle of the wooden part, avoiding holding it too close to either end, to prevent wrist pain and fatigue over time
- Maintain a light grip on the pencil and release any unnecessary pressure on your fingers while writing or drawing. This practice helps prevent hand cramps and fatigue, and regular breaks can also be beneficial.
- Encourage your child to practice holding the pencil in various ways to strengthen their grasp.
Draw and Color
Drawing and coloring activities are an excellent method to nurture children’s handwriting skills. Drawing serves as a means for children to refine their fine motor skills and synchronize hand movements with their visual perception. Similarly, coloring provides a relaxing outlet for children to unwind after a day of school activities.
Through drawing exercises, children unleash their creativity and cultivate essential penmanship habits. These activities reinforce fundamental concepts such as symmetry, balance, composition, and color theory, laying a solid foundation for handwriting development.
Scissor Time
Scissor time presents an excellent opportunity to introduce children to the proper use of scissors. Start by demonstrating how to hold the scissors correctly, then encourage your child to mimic your actions.
Emphasize the importance of safety by demonstrating how to position fingers away from the blades to prevent tearing the paper and ensure they cut in the direction away from themselves. Safety measures are paramount! This activity serves as a highly effective finger exercise for kids, fostering the development of motor skills and enhancing hand-eye coordination.
Next Steps for Developing Your Child’s Motor Skills
Incorporating these handwriting exercises into your child’s routine can support their writing development and boost their confidence. If your child continues to struggle with handwriting, don’t hesitate to schedule an appointment with Ability Rehabilitation. Our experienced therapists are here to provide personalized support and guidance.